Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) occurs when cholesterol-based plaque builds up in the arteries, restricting blood flow, particularly to the legs.
If left untreated, PAD can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life, leading to serious complications.
As there are many risk factors for PAD, with diabetes being particularly significant, early screening is crucial. Early detection provides an opportunity for timely treatment and lifestyle modifications to effectively manage the condition.

What is Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
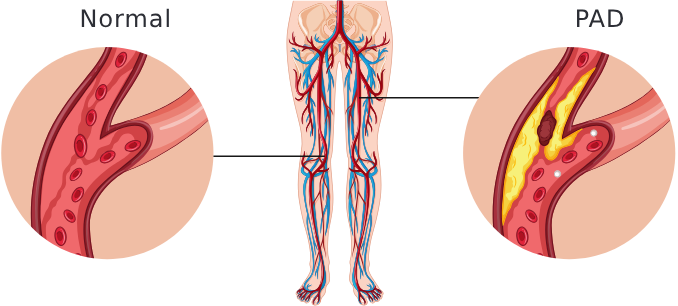
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is due to buildup of plaque within the arteries.
Plaque is composed of cholesterol, fat, calcium-accumulate on the inner walls of the arteries. Over time, this buildup narrows and stiffens the arteries, reducing blood flow to the extremities, typically the legs.
When the blood supply to the legs is disrupted, the muscles do not receive sufficient oxygen and nutrition.
Who is at risk of PAD?
The risk factors for PAD are similar to those for coronary artery disease, and they include:
- Family history of heart disease, stroke, PAD
- History of smoking
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Age 60 and above
What are the Symptoms?
- Leg pain or cramping, especially during activities like walking or climbing stairs
- Leg weakness
- Coldness in legs, a sign of reduced blood flow
- Pale or blueish skin colour
- Slow wound healing
Peripheral Artery Disease Checklist
Do you experience fatigue, heaviness, tiredness or camping in the legs whilst walking or climbing stairs?
- Do you have pain in your legs and/or feet that disturbs your sleep?
- Do you have sores or wounds on your toes, feet or legs that heal slowly, poorly, or not at all?
- Do you have a personal history of vascular disease, heart attack, or stroke?
- Do you have a history of smoking?
- Do you have diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol?
If you answered ‘yes’ to any of these questions on the checklist, you have an increased risk of developing PAD. Early detection of PAD can prevent further cardiovascular events from occurring.
Why is Vascular Screening important? (PAD)?
PAD often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Vascular screening is crucial because it can detect PAD before symptoms appear, allowing for early intervention and management.
By identifying PAD early, healthcare providers can provide lifestyle modifications and medical treatments that help manage symptoms and improve the individual’s quality of life.
Additionally, early intervention can also reduce healthcare costs by preventing more severe complications that require expensive treatments later on.
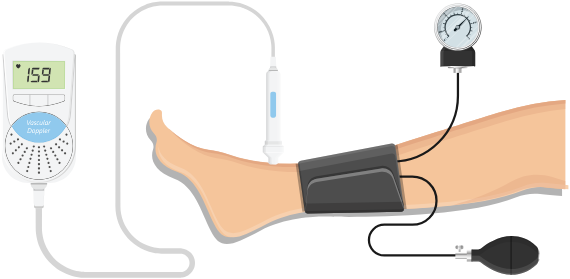
How to detect PAD?
Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) test is a simple, non-invasive test that measures blood pressure at the lower and upper extremities. If the ankle pressure is lower than the arm pressure, it may indicate the presence of PAD.
Ultrasound Doppler uses ultrasound to assess blood flow in the legs, helping to detect any blockages or reduced circulation.
CT Angiogram is an advanced imaging test that provides a detailed view of the arteries, allowing doctors to identify and assess the severity of blockages.
What if I have PAD?
Lifestyle Modification
Lifestyle changes are essential to managing PAD and delaying its complications. Key steps include quitting smoking, following a healthy diet, losing weight and exercising regularly.
Medications
Medications, such as statins to lower cholesterol or blood thinners to prevent clots, may be prescribed to reduce the risk of sudden blockages.
Balloon Angioplasty / Stenting
This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a stent using a balloon to widen narrowed vessels and improve blood flow.
Bypass Surgery
In this procedure, a healthy blood vessel is taken and used to create a “bypass” around the blocked artery, restoring blood flow.
Schedule a consultation with our vascular specialists for more information on vascular diseases.




